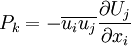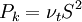Zeta-f model
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
Mirzapopovac (Talk | contribs) |
m (Reverted edits by TadelBasno (Talk) to last version by Jola) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | The ''zeta-f'' model is a robust modification of the elliptic relaxation model. | + | The ''zeta-f'' model is a robust modification of the elliptic relaxation model. For the incompressible Newtonian fluid the final set of equations constituting the <math>\zeta-f</math> model is given below. |
| - | + | == Turbulent viscosity <math>\nu_t</math> == | |
<math>\nu_t = C_\mu \, \zeta \, k \, T</math> | <math>\nu_t = C_\mu \, \zeta \, k \, T</math> | ||
| - | + | == Turbulent kinetic energy <math>k</math> == | |
| - | + | ||
<math>\frac{\partial k}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} = P_k - \varepsilon + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{k}} \right) \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | <math>\frac{\partial k}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} = P_k - \varepsilon + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{k}} \right) \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | ||
| - | + | == Turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate <math>\varepsilon</math> == | |
| - | + | ||
<math>\frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} = \frac{C_{\varepsilon 1} P_k - C_{\varepsilon 2} \varepsilon}{T} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\varepsilon}} \right) \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | <math>\frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} = \frac{C_{\varepsilon 1} P_k - C_{\varepsilon 2} \varepsilon}{T} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\varepsilon}} \right) \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | ||
| - | + | == Normalized velocity scale <math>\zeta</math> == | |
| - | + | ||
<math>\frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} = f - \frac{\zeta}{k} P_k + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\zeta}} \right) \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | <math>\frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} = f - \frac{\zeta}{k} P_k + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\zeta}} \right) \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | ||
| - | + | == Elliptic relaxation function <math>f</math> == | |
| - | + | ||
<math>L^2 \nabla^2 f - f = \frac{1}{T} \left( C_1 - 1 + C'_2 \frac{P_k}{\varepsilon} \right) \left( \zeta - \frac{2}{3} \right)</math> | <math>L^2 \nabla^2 f - f = \frac{1}{T} \left( C_1 - 1 + C'_2 \frac{P_k}{\varepsilon} \right) \left( \zeta - \frac{2}{3} \right)</math> | ||
| + | == Production of the turbulent kinetic energy <math>P_k</math> == | ||
| - | + | :<math> | |
| + | P_k = - \overline{u_i u_j} \frac{\partial U_j}{\partial x_i} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | :<math> P_k = \nu_t S^2 </math> | ||
| - | <math> | + | == Modulus of the mean rate-of-strain tensor <math>S</math> == |
| + | <math>S \equiv \sqrt{2S_{ij} S_{ij}}</math> | ||
| - | + | == Turbulence time scale <math>T</math> == | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>T = max \left[ min \left( \frac{k}{\varepsilon},\, \frac{0.6}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S|\zeta} \right), C_T \left( \frac{\nu}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/2} \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Turbulence length scale <math>L</math> == | ||
<math>L = C_L \, max \left[ min \left( \frac{k^{3/2}}{\varepsilon}, \, | <math>L = C_L \, max \left[ min \left( \frac{k^{3/2}}{\varepsilon}, \, | ||
| Line 38: | Line 44: | ||
\left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/4} \right]</math> | \left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/4} \right]</math> | ||
| - | + | == Model coefficients == | |
| - | + | ||
<math>C_\mu = 0.22</math>, <math>\sigma_{k} = 1</math>, <math>\sigma_{\varepsilon} = 1.3</math>, <math>\sigma_{\zeta} = 1.2</math>, <math>C_{\varepsilon 1} = 1.4 (1 + 0.012 / \zeta)</math>, <math>C_{\varepsilon 2} = 1.9</math>, <math>C_1 = 1.4</math>, <math>C_2' = 0.65</math>, <math>C_T = 6</math>, <math>C_L = 0.36</math> and <math>C_{\eta} = 85</math>. | <math>C_\mu = 0.22</math>, <math>\sigma_{k} = 1</math>, <math>\sigma_{\varepsilon} = 1.3</math>, <math>\sigma_{\zeta} = 1.2</math>, <math>C_{\varepsilon 1} = 1.4 (1 + 0.012 / \zeta)</math>, <math>C_{\varepsilon 2} = 1.9</math>, <math>C_1 = 1.4</math>, <math>C_2' = 0.65</math>, <math>C_T = 6</math>, <math>C_L = 0.36</math> and <math>C_{\eta} = 85</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *<b>Popovac, M., Hanjalic, K.</b> Compound Wall Treatment for RANS Computation of Complex Turbulent Flows and Heat Transfer, Flow Turbulence and Combustion, 78, 177-202, 2007. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *<b>Hanjalic, K., Popovac, M., Hadziabdic, M.</b> A robust near-wall elliptic-relaxation eddy-viscosity turbulence model for CFD, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 25, 1047–1051, 2004. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Turbulence models]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:06, 17 December 2008
The zeta-f model is a robust modification of the elliptic relaxation model. For the incompressible Newtonian fluid the final set of equations constituting the 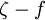 model is given below.
model is given below.
Turbulent viscosity 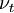
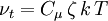
Turbulent kinetic energy 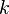
![\frac{\partial k}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} = P_k - \varepsilon + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{k}} \right) \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} \right]](/W/images/math/4/e/a/4eac951b79fdf4d26cac2b6cca1540bd.png)
Turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate 
![\frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} = \frac{C_{\varepsilon 1} P_k - C_{\varepsilon 2} \varepsilon}{T} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\varepsilon}} \right) \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} \right]](/W/images/math/5/b/e/5be411c44d64810a0a4d341ada81137c.png)
Normalized velocity scale 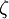
![\frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} = f - \frac{\zeta}{k} P_k + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\zeta}} \right) \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} \right]](/W/images/math/1/4/3/143979f772a60676f05d24a868fa7f47.png)
Elliptic relaxation function 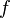
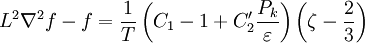
Production of the turbulent kinetic energy 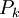
Modulus of the mean rate-of-strain tensor 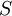
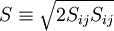
Turbulence time scale 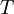
![T = max \left[ min \left( \frac{k}{\varepsilon},\, \frac{0.6}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S|\zeta} \right), C_T \left( \frac{\nu}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/2} \right]](/W/images/math/e/0/b/e0b175df5f22a619bce6dbf7ebf46775.png)
Turbulence length scale 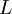
![L = C_L \, max \left[ min \left( \frac{k^{3/2}}{\varepsilon}, \,
\frac{k^{1/2}}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S| \zeta} \right), C_{\eta}
\left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/4} \right]](/W/images/math/7/0/7/70730f002515f1c28758512281d69cd2.png)
Model coefficients
 ,
, 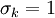 ,
, 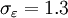 ,
,  ,
, 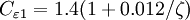 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 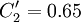 ,
,  ,
, 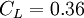 and
and  .
.
References
- Popovac, M., Hanjalic, K. Compound Wall Treatment for RANS Computation of Complex Turbulent Flows and Heat Transfer, Flow Turbulence and Combustion, 78, 177-202, 2007.
- Hanjalic, K., Popovac, M., Hadziabdic, M. A robust near-wall elliptic-relaxation eddy-viscosity turbulence model for CFD, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 25, 1047–1051, 2004.