Turbulence modeling
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Content of turbulence modeling section) |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | # [[Turbulence]] | + | Turbulence modeling is a key issue in most CFD simulations. Virtually all engineering applications are turbulent and hence require a turbulence model. |
| - | # [[Algebraic turbulence models|Algebraic models]] | + | |
| - | ##[[Cebeci-Smith model]] | + | ==Classes of turbulence models== |
| - | ##[[Baldwin-Lomax model]] | + | |
| - | ## [[Johnson-King model]] | + | *RANS-based models |
| - | # [[One equation models]] | + | **Linear eddy-viscosity models |
| - | ## [[Prandtl's one-equation model]] | + | ***Algebraic models |
| - | ## [[Baldwin-Barth model]] | + | ***One and two equation models |
| - | ## [[Spalart-Allmaras model]] | + | **Non-linear eddy viscosity models and algebraic stress models |
| - | # [[Two equation models]] | + | **Reynolds stress transport models |
| - | ## [[k-epsilon models]] | + | |
| - | ### [[Standard k-epsilon model]] | + | *Large eddy simulations |
| - | ### [[ | + | |
| - | ### [[RNG k-epsilon model]] | + | *Detached eddy simulations and other hybrid models |
| - | ### [[Near-wall treatment for k-epsilon models]] | + | |
| - | ## [[k-omega models]] | + | *Direct numerical simulations |
| - | ### [[Wilcox's k-omega model]] | + | |
| - | ### [[Wilcox's modified k-omega model]] | + | ==Content of turbulence modeling section== |
| - | ### [[SST k-omega model]] | + | |
| - | ### [[Near-wall treatment for k-omega models]] | + | # '''[[Turbulence]]''' |
| - | ## [[Two equation turbulence model constraints and limiters]] | + | # '''[[RANS-based turbulence models]]''' |
| - | ### [[Kato-Launder modification]] | + | ## '''''[[Linear eddy viscosity models]]''''' |
| - | ### [[Durbin's realizability constraint]] | + | ### ''[[Algebraic turbulence models|Algebraic models]]'' |
| - | ### [[Yap correction]] | + | #### [[Cebeci-Smith model]] |
| - | # [[v2-f models]] | + | #### [[Baldwin-Lomax model]] |
| - | ## <math>\overline{\upsilon^2}-f</math> model | + | #### [[Johnson-King model]] |
| - | ## <math>\zeta-f</math> model | + | #### [[A roughness-dependent model]] |
| - | # [[Reynolds stress model (RSM) ]] | + | ### ''[[One equation turbulence models|One equation models]]'' |
| - | # [[Large eddy simulation (LES) ]] | + | #### [[Prandtl's one-equation model]] |
| + | #### [[Baldwin-Barth model]] | ||
| + | #### [[Spalart-Allmaras model]] | ||
| + | #### [[Rahman-Agarwal-Siikonen Model]] | ||
| + | #### [[Wray-Agarwal(WA) turbulence Model]] | ||
| + | #### [[Shuai-Agarwal turbulence Model]] | ||
| + | ### ''[[Two equation models]]'' | ||
| + | #### [[k-epsilon models]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Standard k-epsilon model]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Realizable k-epsilon model]] | ||
| + | ##### [[RNG k-epsilon model]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Near-wall treatment for k-epsilon models|Near-wall treatment]] | ||
| + | #### [[k-omega models]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Wilcox's k-omega model]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Wilcox's modified k-omega model]] | ||
| + | ##### [[SST k-omega model]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Near-wall treatment for k-omega models|Near-wall treatment]] | ||
| + | #### [[Two equation turbulence model constraints and limiters|Realisability issues]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Kato-Launder modification]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Durbin's realizability constraint]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Yap correction]] | ||
| + | ##### [[Realisability and Schwarz' inequality]] | ||
| + | ## '''''[[Nonlinear eddy viscosity models]]''''' | ||
| + | ### [[Explicit nonlinear constitutive relation]] | ||
| + | #### [[Cubic k-epsilon]] | ||
| + | #### [[Explicit algebraic Reynolds stress models (EARSM)]] | ||
| + | ### [[v2-f models]] | ||
| + | #### <math>\overline{\upsilon^2}-f</math> model | ||
| + | #### <math>\zeta-f</math> model | ||
| + | ## '''''[[Reynolds stress model (RSM) ]]''''' | ||
| + | # '''[[Large eddy simulation (LES) ]]''' | ||
## [[Smagorinsky-Lilly model]] | ## [[Smagorinsky-Lilly model]] | ||
## [[Dynamic subgrid-scale model]] | ## [[Dynamic subgrid-scale model]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 64: | ||
## [[Kinetic energy subgrid-scale model]] | ## [[Kinetic energy subgrid-scale model]] | ||
## [[Near-wall treatment for LES models]] | ## [[Near-wall treatment for LES models]] | ||
| - | # [[Detached eddy simulation (DES) ]] | + | ## [[Structural modeling]] |
| - | # [[Direct numerical simulation (DNS) ]] | + | # '''[[Detached eddy simulation (DES) ]]''' |
| - | # [[Turbulence near-wall modeling]] | + | # '''[[Direct numerical simulation (DNS) ]]''' |
| - | # [[Turbulence free-stream boundary conditions]] | + | # '''[[Turbulence near-wall modeling]]''' |
| + | # '''[[Turbulence free-stream boundary conditions]]''' | ||
## [[Turbulence intensity]] | ## [[Turbulence intensity]] | ||
| - | ## [[ | + | ## [[Turbulence length scale]] |
[[Category:Turbulence models]] | [[Category:Turbulence models]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:16, 10 April 2021
Turbulence modeling is a key issue in most CFD simulations. Virtually all engineering applications are turbulent and hence require a turbulence model.
Classes of turbulence models
- RANS-based models
- Linear eddy-viscosity models
- Algebraic models
- One and two equation models
- Non-linear eddy viscosity models and algebraic stress models
- Reynolds stress transport models
- Linear eddy-viscosity models
- Large eddy simulations
- Detached eddy simulations and other hybrid models
- Direct numerical simulations
Content of turbulence modeling section
- Turbulence
- RANS-based turbulence models
- Large eddy simulation (LES)
- Detached eddy simulation (DES)
- Direct numerical simulation (DNS)
- Turbulence near-wall modeling
- Turbulence free-stream boundary conditions

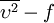 model
model
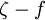 model
model