Dimensionless wall distance (y plus)
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A non-dimensional wall distance for a wall-bounded flow can be defined in the following way: | A non-dimensional wall distance for a wall-bounded flow can be defined in the following way: | ||
| - | :<math>y^+ \equiv \frac{u_* | + | :<math>y^+ \equiv \frac{u_* \, y}{\nu}</math> |
Where <math>u_*</math> is the [[Friction velocity|friction velocity]] at the nearest wall, <math>y</math> is the distance to the nearest wall and <math>\nu</math> is the local [[Kinematic viscosity|kinematic viscosity]] of the fluid. | Where <math>u_*</math> is the [[Friction velocity|friction velocity]] at the nearest wall, <math>y</math> is the distance to the nearest wall and <math>\nu</math> is the local [[Kinematic viscosity|kinematic viscosity]] of the fluid. | ||
Revision as of 15:11, 11 May 2006
A non-dimensional wall distance for a wall-bounded flow can be defined in the following way:
Where 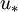 is the friction velocity at the nearest wall,
is the friction velocity at the nearest wall, 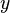 is the distance to the nearest wall and
is the distance to the nearest wall and 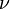 is the local kinematic viscosity of the fluid.
is the local kinematic viscosity of the fluid.
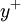 is often refered to simply as y plus and is commonly used in boundary layer theory and in defining the law of the wall.
is often refered to simply as y plus and is commonly used in boundary layer theory and in defining the law of the wall.

