Zeta-f model
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
Mirzapopovac (Talk | contribs) |
Mirzapopovac (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | The ''zeta-f'' model is a robust modification of the elliptic relaxation model. The set of equations constituting the <math>\zeta-f</math> model reads: | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The turbulent viscosity | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\nu_t = C_\mu \, \zeta \, k \, T</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The turbulent kinetic energy <math>k</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial k}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} = P_k - \varepsilon + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{k}} \right) \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate <math>\varepsilon</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} = \frac{C_{\varepsilon 1} P_k - C_{\varepsilon 2} \varepsilon}{T} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\varepsilon}} \right) \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The normalized fluctuating velocity normal to the streamlines <math>\zeta</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} = f - \frac{\zeta}{k} P_k + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\zeta}} \right) \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The elliptic relaxation function <math>f</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>L^2 \nabla^2 f - f = \frac{1}{T} \left( C_1 - 1 + C'_2 \frac{P_k}{\varepsilon} \right) \left( \zeta - \frac{2}{3} \right)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The turbulence time scale <math>T</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>T = max \left[ min \left( \frac{k}{\varepsilon},\, \frac{0.6}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S|\zeta} \right), C_T \left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/2} \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The turbulence length scale <math>L</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>L = C_L \, max \left[ min \left( \frac{k^{3/2}}{\varepsilon}, \, | ||
| + | \frac{k^{1/2}}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S| \zeta} \right), C_{\eta} | ||
| + | \left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/4} \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The coefficients | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>C_\mu = 0.22</math>, <math>\sigma_{k} = 1</math>, <math>\sigma_{\varepsilon} = 1.3</math>, <math>\sigma_{\zeta} = 1.2</math>, <math>C_{\varepsilon 1} = 1.4 (1 + 0.012 / \zeta)</math>, <math>C_{\varepsilon 2} = 1.9</math>, <math>C_1 = 1.4</math>, <math>C_2' = 0.65</math>, <math>C_T = 6</math>, <math>C_L = 0.36</math> and <math>C_{\eta} = 85</math>. | ||
Revision as of 11:06, 22 January 2007
The zeta-f model is a robust modification of the elliptic relaxation model. The set of equations constituting the 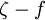 model reads:
model reads:
The turbulent viscosity
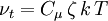
The turbulent kinetic energy 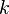
![\frac{\partial k}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} = P_k - \varepsilon + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{k}} \right) \frac{\partial k}{\partial x_j} \right]](/W/images/math/4/e/a/4eac951b79fdf4d26cac2b6cca1540bd.png)
The turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate 
![\frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} = \frac{C_{\varepsilon 1} P_k - C_{\varepsilon 2} \varepsilon}{T} + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\varepsilon}} \right) \frac{\partial \varepsilon}{\partial x_j} \right]](/W/images/math/5/b/e/5be411c44d64810a0a4d341ada81137c.png)
The normalized fluctuating velocity normal to the streamlines 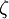
![\frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial t} + U_j \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} = f - \frac{\zeta}{k} P_k + \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j} \left[ \left( \nu + \frac{\nu_t}{\sigma_{\zeta}} \right) \frac{\partial \zeta}{\partial x_j} \right]](/W/images/math/1/4/3/143979f772a60676f05d24a868fa7f47.png)
The elliptic relaxation function 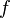
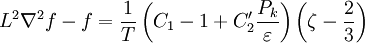
The turbulence time scale 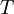
![T = max \left[ min \left( \frac{k}{\varepsilon},\, \frac{0.6}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S|\zeta} \right), C_T \left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/2} \right]](/W/images/math/6/1/7/617b18437b40d1988d1ca62041a1bca0.png)
The turbulence length scale 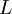
![L = C_L \, max \left[ min \left( \frac{k^{3/2}}{\varepsilon}, \,
\frac{k^{1/2}}{\sqrt{6} C_{\mu} |S| \zeta} \right), C_{\eta}
\left( \frac{\nu^3}{\varepsilon} \right)^{1/4} \right]](/W/images/math/7/0/7/70730f002515f1c28758512281d69cd2.png)
The coefficients
 ,
, 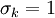 ,
, 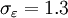 ,
,  ,
, 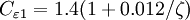 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 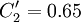 ,
,  ,
, 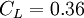 and
and  .
.
