K-epsilon models
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
Tohoughton (Talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
Tohoughton (Talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The first transported variable is turbulent kinetic energy, <math>k</math>. The second transported variable in this case is the turbulent dissipation, <math>\epsilon</math>. It is the variable that determines the scale of the turbulence, whereas the first variable, <math>k</math>, determines the energy in the turbulence. | The first transported variable is turbulent kinetic energy, <math>k</math>. The second transported variable in this case is the turbulent dissipation, <math>\epsilon</math>. It is the variable that determines the scale of the turbulence, whereas the first variable, <math>k</math>, determines the energy in the turbulence. | ||
| - | To calculate boundary conditions for a calculation using | + | To calculate boundary conditions for a calculation using these models see [[Turbulence free-stream boundary conditions|turbulence free-stream boundary conditions]]. |
== Usual K-epsilon models == | == Usual K-epsilon models == | ||
Revision as of 09:14, 15 May 2008
Introduction
The K-epsilon model is one of the most common turbulence models. It is a two equation model, that means, it includes two extra transport equations to represent the turbulent properties of the flow. This allows a two equation model to account for history effects like convection and diffusion of turbulent energy.
The first transported variable is turbulent kinetic energy, 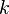 . The second transported variable in this case is the turbulent dissipation,
. The second transported variable in this case is the turbulent dissipation,  . It is the variable that determines the scale of the turbulence, whereas the first variable,
. It is the variable that determines the scale of the turbulence, whereas the first variable, 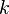 , determines the energy in the turbulence.
, determines the energy in the turbulence.
To calculate boundary conditions for a calculation using these models see turbulence free-stream boundary conditions.
Usual K-epsilon models
Miscellaneous

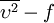 model
model
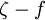 model
model